

Time:2026-01-30 Views:1
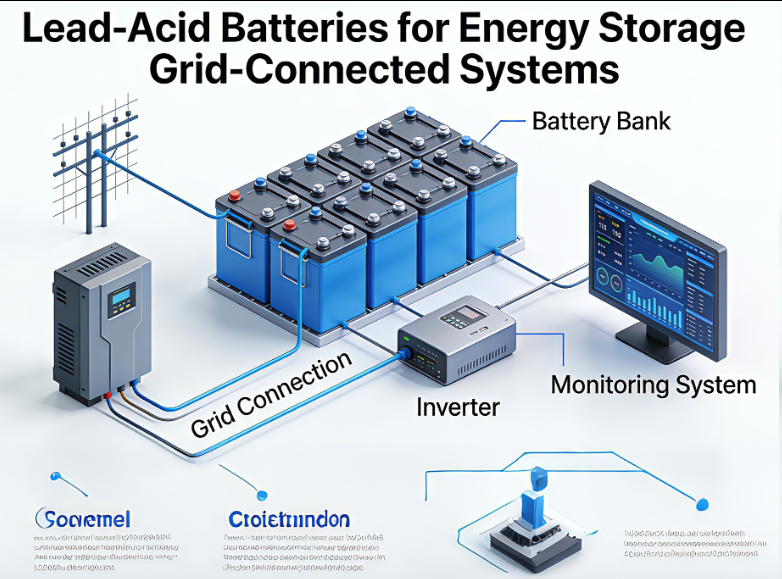
Lead-acid batteries play a vital role in grid-connected energy storage systems, serving as a reliable and cost-effective solution for storing excess electricity generated from renewable sources or grid peaking, and enabling seamless integration with the electrical grid. These systems, which connect to the utility grid, use lead-acid batteries to store energy during periods of low demand or high renewable generation (such as midday for solar) and discharge it during peak demand hours, helping to balance grid load, stabilize voltage, and reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based power plants.
One of the key advantages of lead-acid batteries in grid-connected systems is their mature technology and proven performance. They have a long history of use in stationary applications, with well-understood charging and discharging characteristics that make them compatible with grid management systems. Lead-acid batteries can handle deep discharge cycles, which is essential for grid storage, where maximizing energy extraction is critical. They also offer rapid response times, allowing them to quickly inject power into the grid during sudden demand spikes or renewable generation lulls, enhancing grid stability.
Integration of lead-acid batteries into grid-connected systems requires compatibility with inverters, which convert the battery’s DC power to AC for grid use, and advanced energy management systems (EMS) that optimize charging and discharging based on grid conditions, electricity prices, and renewable generation forecasts. The EMS ensures that the batteries are charged when electricity is cheapest or most abundant (e.g., during high solar output) and discharged when prices are highest or demand peaks, maximizing economic benefits for system operators.
Lead-acid batteries in grid-connected systems also contribute to grid resilience by providing backup power during outages, ensuring continuity of supply for critical infrastructure such as hospitals, data centers, and communication networks. Their ability to operate in a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions makes them suitable for deployment in diverse locations, from urban substations to remote renewable energy farms.
Despite competition from newer battery technologies like lithium-ion, lead-acid batteries remain a popular choice for grid-connected storage due to their lower upfront costs, ease of maintenance, and high recyclability. The lead-acid battery recycling rate exceeds 95% in many countries, making them an environmentally sustainable option compared to batteries with limited recycling infrastructure. As grid modernization efforts continue and renewable energy adoption grows, lead-acid batteries are expected to remain a key component of grid-connected energy storage systems, offering a balance of performance, cost, and reliability.
Read recommendations:
Solid - State Battery Manufacturing Processes